Bayesian _______
estimation
The
problem is the quality of a 5 star rating depends not only on
the average number of stars but also on the number of reviews. Bayesian
estimation attempts to forgo computing a direct value from a limited
number of observations and
instead creates a probability distribution. It would seem clear that a
4.1-star rating with hundreds of reviewers has many that are happy.
Therefore, it should probably
appear before a 5-star rating with only one reviewer even though its
average rating is lower. Bayes formula tells us how to compute the
probability of
X given O: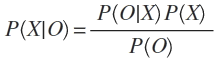
model
A Bayesian model can explicitly account for:- Time. Perhaps old ratings should count for less than new ratings.
- Prior beliefs. Perhaps an unrated item from a bestselling author should appear above an unrated item from an unknown author.
- Attitudes toward risk. Exactly how risk-averse should the algorithm be about promoting items with a small number ratings?
trap
"The Bayesian Trap" Veritasium on YouTube. Bayes' theorem explained with examples and implications for life.logic
Combine probabilistic logic and Bayesian networks to obtain the advantages of each in what is called Bayesian logic. Like probabilistic logic, it is a theoretically grounded way of representing and reasoning with uncertainty that uses only as much probabilistic information as one has, since it permits one to specify probabilities as intervals rather than precise values.network
A Bayesian network is an augmented, directed acyclic graph, where each node corresponds to a random variable x and each edge indicates a direct influence among the random variables.probability
Bayesian probability is an interpretation of the concept of probability, in which, instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon, probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief.statistics
Bayesian statistics is a mathematical procedure that applies probabilities to statistical problems.source: Bayesian Statistics explained to Beginners in Simple English
analysis
Bayesian analysis is a statistical paradigm that answers research questions about unknown parameters using probability statements. In Bayesian analysis, a parameter is summarized by an entire distribution of values instead of one fixed value as in classical frequentist analysis. Unique features of Bayesian analysis include an ability to incorporate prior information in the analysis, an intuitive interpretation of credible intervals as fixed ranges to which a parameter is known to belong with a prespecified probability, and an ability to assign an actual probability to any hypothesis of interest.inference
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available.Bayes’ theorem
Bayes’ theorem describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if cancer is related to age, then, using Bayes’ theorem, a person’s age can be used to more accurately assess the probability that they have cancer, compared to the assessment of the probability of cancer made without knowledge of the person's age.Named for Thomas Bayes, an English clergyman and mathematician, Bayesian logic is a branch of logic applied to decision making and inferential statistics that deals with probability inference: using the knowledge of prior events to predict future events.
No comments:
Post a Comment